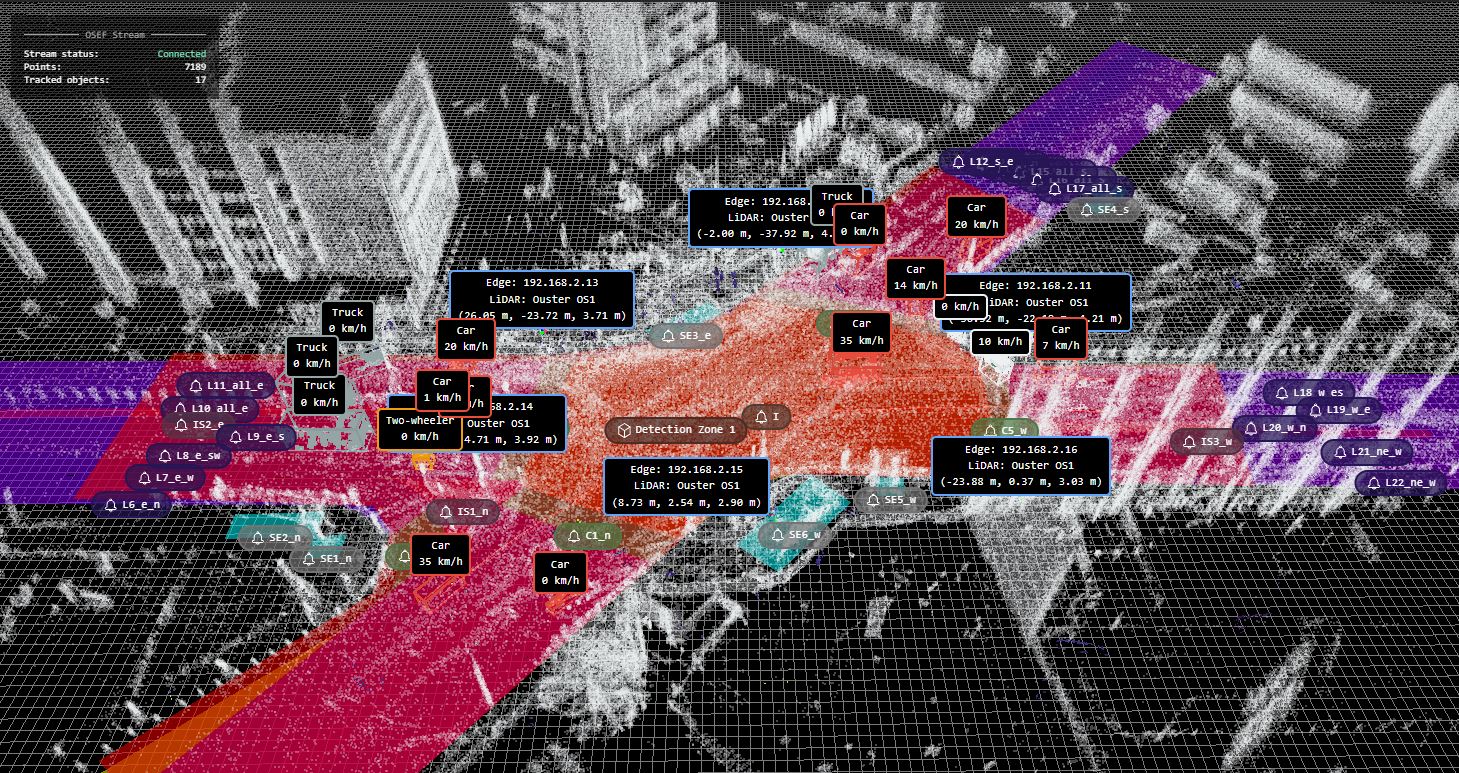
Traffic Monitoring and Simulation
Leveraging the traffic data obtained through monitoring one of the busiest intersections in Sofia city, this study workflow shows the effective integration of LiDAR data and the urban digital twin concept in intelligent transportation systems (ITS). The research addresses problems related to moving object classification, trajectory analysis, and reclassification of unrecognised objects by processing the LiDAR data, pre-processed in a .osef format, thereby transforming it to make it suitable for simulation. The proposed solution for the monitoring of urban traffic is demonstrated by the usage of SUMO (Simulation of Urban MObility) for performing simulations and a Random Forest model for unrecognized object reclassification to pre-existing vehicles and pedestrian classes.
Trajectory type plot of each object consist of complete, (short) complete, violation, and incomplete track.
The data includes three categories of objects: recognized objects (one unknown among two classes, classified as the known class), consistent objects (single class), and unidentified objects (changing classes more than twice). The Random Forest model is trained using two distinct .osef datasets, one from an afternoon session lasting four minutes and the other from a morning session lasting two minutes, comprising 108,156 frames.
To simulate traffic in real-time, the traffic simulation program SUMO fetches a parsed dataset. There are two types of simulation experiments: xml based and dynamic using TraCI. To map-match incomplete trajectories to the SUMO road network, the data fetch function additionally includes the map-match logic utilizing sumolib. By comparing the incomplete trajectories with the missing sequences, this map-matching algorithm finds the edges and lanes that are closest to the end or starting point.
The architecture of the proposed workflow can possibly be applied in other similar urban settings, providing a scalable solution for both traffic management and urban planning. The study’s results support the wider use of urban digital twin principles in ITS by highlighting the value of advanced modelling tools and high-quality data in addressing today's urban transportation challenges.

